Compact Bone Structure - YouTube. Spongy bone is also called cancellous or trabecular bone.

Forms the epiphyses ends of long bones.
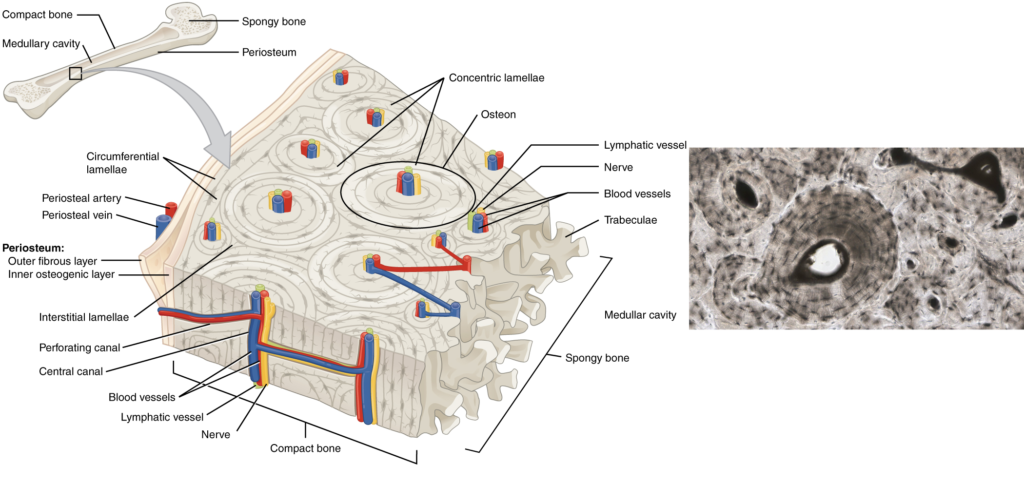
Where do you find compact bone. Compact Bone It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones where it provides support and protection. The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae singular lamella.
Compact bone makes up 80 percent of the human skeleton. The remainder is cancellous bone which has a spongelike appearance with numerous large spaces and is found in the marrow space medullary cavity of a bone. Both types are found in most bones.
Compact bone forms a shell around cancellous bone and is the primary component of the long bones of the arm and leg and other bones where its. Compact Bone Definition. Compact bone also known as cortical bone is a denser material used to create much of the hard structure of the skeleton.
As seen in the image below compact bone forms the cortex or hard outer shell of most bones in the body. The remainder of the bone is formed by cancellous or spongy bone. Under magnification you can clearly see the system of concentric circles that forms compact bone.
You can think of compact bone as being very similar to a bundle of cut trees or logs. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of osseous tissue Figure 636. It makes up the outer cortex of all bones and is in immediate contact with the periosteum.
In long bones as you move from the outer cortical compact bone to the. Compact bone is sometimes called cortical bone. At the outer edges of compact bone rather than being arranged in osteons the osseous tissue is arranged in circumferential lamellae.
These travel parallel to the outer edge of the bone and are usually only a few lamellae deep before the osteons start up. The bones of the body only have compact bone on their outermost surfaces and never very deep. Compact bone is the heaviest hardest type of bone.
It needs to be very strong as it supports your body and muscles as you walk run and move throughout the day. About 80 of the bone in your body is compact. It makes up the outer layer of the bone and also helps protect the more fragile layers inside.
Spongy bone is also called cancellous or trabecular bone. It is found in the long bones and it is surrounded by compact bone. The term spongy comes from the fact that it is a highly vascularized and porous tissue.
Trabeculae are spaces created in the tissue by thin areas of osteoblast cells. Compact Cortical Bone Spongy Cancellous Bone. Also called as cortical bones.
Also called as cancellous bones. They are compact heavy and tough in nature. They are spongy light and soft in nature.
Forms the diaphysis shaft of long bones. Forms the epiphyses ends of long bones. Compact bones fills the outer layers of most of the bones.
Throughout compact bone oriented parallel to the long axis of the bone or in the direction of applied force. Like compact bone spongy bone also known as cancellous bone contains osteocytes housed in lacunae but they are not arranged in concentric circles. Instead the lacunae and osteocytes are found in a lattice-like network of matrix spikes called trabeculae singular trabecula Figure 613.
Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of bone tissue. It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones where it provides support and protection. Compact bones occur in the inner surface of a bone.
Spongy bones occur in the outer layers of a bone. Compact bones can withstand the weight of up to 5000 pounds. Spongy bones are unable to withstand high weights.
Compact bones provide structural support to the body. Compact bones are the present in the outer layer of long bones while spongy bones are present in the middle of the long bones. The main difference between spongy and compact bones is their structure and function.
Visit BYJUS to learn more differences. Compact Bone Structure - YouTube. The compact bone gets its white smooth structure owing to the connective tissues that cover around ¾ part of the bone from inside.
The shafts found in long bones are also compact bones. These bones are tough and hard with negligible gaps inside them. Compact and spongy tissues in a.
The key difference between compact bone and spongy bone is that the compact bone is a tough and heavy bone that forms the diaphysis of long bones while the spongy bone is a soft and light bone that forms the epiphysis of long bones. Bones are hard organs inside our bodies that make up our skeletal system. They serve the purpose of protecting our bodies and also provide a structure and.
Compact bone is the harder outer shell of the bone while cancellous bone is the inner porous less dense layers of the bone. Bones are important components in assisting movement and granting a shape to the body. Bones are components of the skeletal system.
The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones. Mainly the human skeleton has two main. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of bone tissue link.
It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones where it provides support and protection. Diagram of Compact Bone. A This cross-sectional view of compact.
Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy cancellous bone has open spaces and supports shifts in weight distribution. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of bone tissue. It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones where it provides support and protection.
The main difference between compact and trabecular bone is that compact bone is a tough and heavy bone made up of compactly packed osteons whereas trabecular bone is a soft and light bone made up of loosely packed trabeculae. Furthermore compact bones make up the shaft of long bones while trabecular bones make up the ends of long bones. Compact and trabecular bone are the two.
An _____ is the basic structural unit of compact bone consisting of a central canal and its lamellae. Osteons Osteocytes Lamellae Interstitial lamella Canaliculi. Osteogenic cells are stem cells in the endosteum periosteum and central canals.