
Perpendicular plate perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The cranial cavity also known as intracranial space is the space within the skull.
Perpendicular plate perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone.
Space inside cranial bone. The cranial cavity also known as intracranial space is the space within the skull. The space inside the skull is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium. The neurocranium is the upper back part that forms the protective case around the brain.
The cranial cavity also known as intracranial space is the space within the skull. The space inside the skull is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium. The neurocranium is the upper back part that forms the protective case around the brain.
CRANIAL CAVITY The cranial cavity is the space within the skull that houses the brain. The skull excluding the mandible is called the cranium. The cavity is formed by 8 cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in humans includes the skull cap and formsthe protective case around the brain.
The cranial cavity is the anterior portion of the dorsal cavity consisting of the space inside the skull. This cavity contains the brain the meninges of the brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Read remaining answer here.
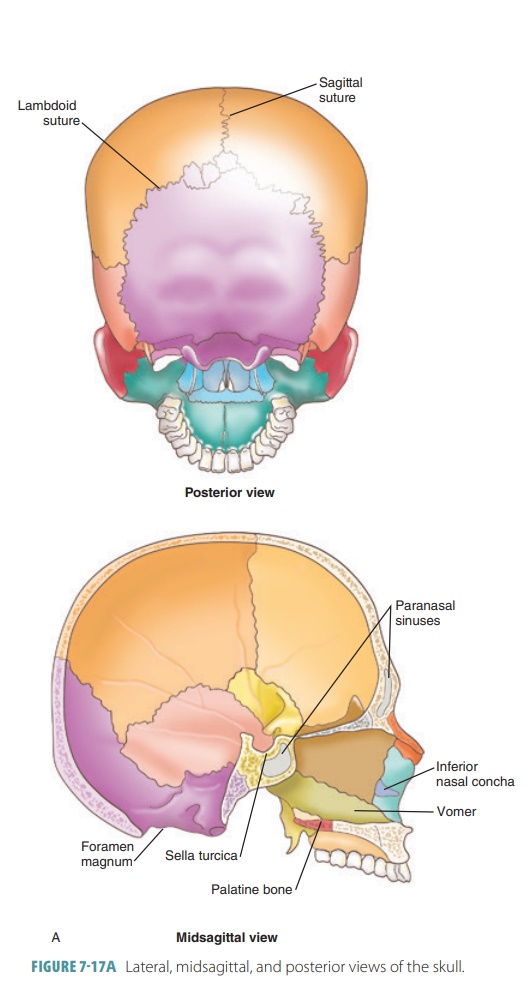
Cranial floor grooves provide space for the cranial sinuses that drain blood and cerebrospinal fluid from the lower regions of the meninges dura mater arachnoid and pia mater the cerebrum and the cerebellum. The neurocranium has several sutures or articulations. The first four in the following list are the most important.
Parietal bones These paired bones form the sides and roof of the cranial cavity-The internal surfaces of the parietal bones contain many protrusions and depressions that accommodate the blood vessels supplying the dura mater a covering of the brain. It spans the width of your skull and forms a large part of the base of your skull. This is an irregular bone located in front of.
The cranial cavity also known as intracranial space is the space within the skull. The space inside the skull is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium. The neurocranium is the upper back part that forms the protective case around the brain.
However in the literature the cranial epidural space itself seems to be disregarded as an anatomical site for bone regeneration studies. In this anatomical site biomaterial particles could be inserted in bursae atraumatically opened between the dura mater and the cranial vault surface at a distance of the bone defect created for accessing. Air-filled spaces inside the cranial bones that help the voice to resonate and also reduce the weight of the skull Frontal bone forms the anterior skull above the eyes.
It is narrow at the apex of the skull but because the arachnoidea follows the pia mater larger caverns are created in areas where the brain and bony cranial wall are further apart at the base of the cranium. These widened CSF-filled spaces are called cisterns cerebromedullar cistern interpeduncular cistern chiasmatic cistern cisterna ambiens. Outgrowths of the arachnoidea the.
The cranial cavity also known as intracranial space is the space within the skull. The space inside the skull is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium. The skull minus the mandible is also known as the cranium and contains the brain.
Click to see full answer. Anterior cranial bone located between the eyes part of the medial wall of the orbit roof and walls of the nasal cavity and the nasal septum. Porous and delicate bone with 3 major parts.
Perpendicular plate perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The distal ends of the extremities the vertebrae and the bones of the face. The cranium may also become larger by eccentric apposition of bone.
The structural appearance of the acromegalic skull is not different from the structure of normal cranial bones. The pneumatic spaces are usually very large acroniegalic liyperpneumatisation. The cranial cavity also known as intracranial space is the space within the skull.
The space inside the skull is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium. The skull minus the mandible is also known as the cranium and contains the brain. Temporal fossa It is a shallow space in between the side of the braincase and above the zygomatic arch level.
Infratemporal fossa It is an area below the zygomatic arch level and deep to the vertical part of the mandible. By atraumatic separation of dura mater from the inner bone surface. The osseous access sites to create epidural spaces were circular and its centers were established 7 mm in the dorsal direction from a point located in the nasofrontal suture and 5 mm lateral respect to the inter-frontal suture Fig.
The bursae were created by separ-.