
The kinematics of the subtalar joint allows the combined motions of inversionadduction and eversionabduction of the rearfoot Fig. Muscles involved in pronation and supination are attached to radius which then moves around the fixed ulna of forearm.
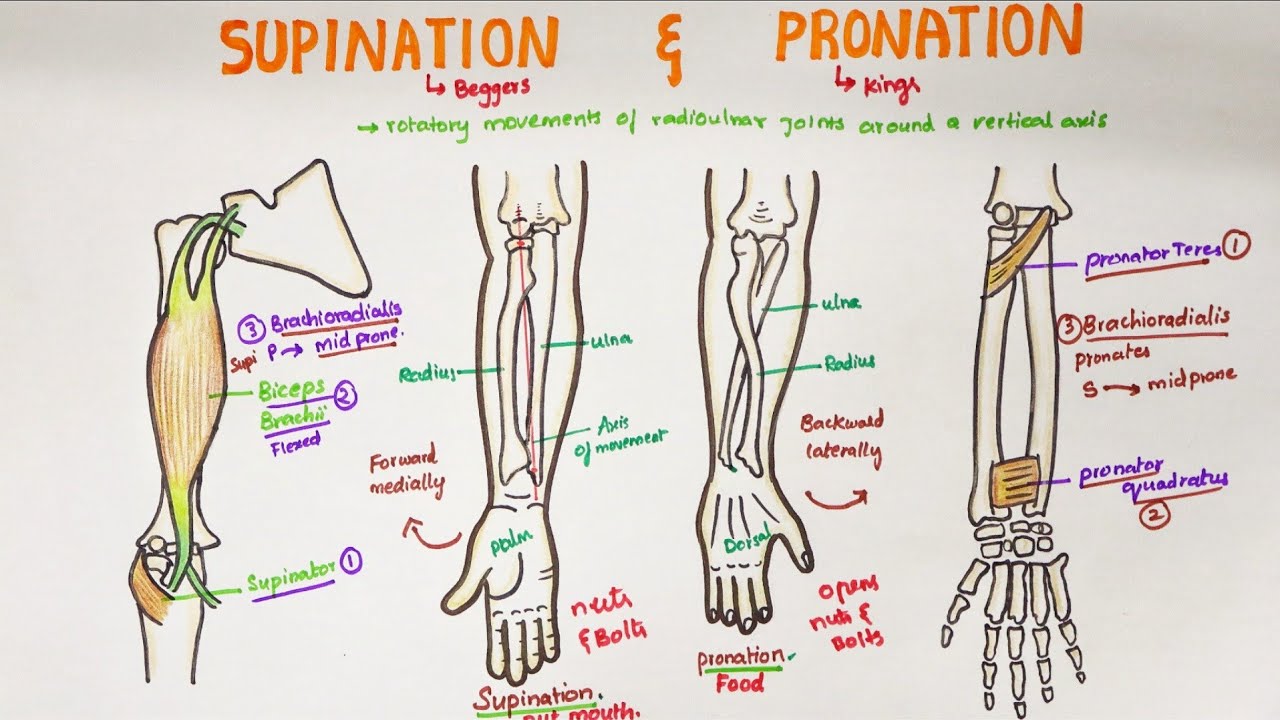
The head of the radius is discoid and fits with the radial neck within the circular annular ligament that attaches the proximal radius to the ulna.
Pronation and supination occur at which joints. Bones and joints. Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the proximal radioulnar joint. The head of the radius is discoid and fits with the radial neck within the circular annular ligament that attaches the proximal radius to the ulna.
Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the proximal radioulnar joint. The head of the radius is discoid and fits with the radial neck within the circular annular ligament that attaches the proximal radius to the ulna. Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the proximal radioulnar joint.
The head of the radius is discoid and fits with the radial neck within the circular annular ligament that attaches the proximal radius to the ulna. Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the proximal radioulnar joint. The head of the radius is discoid and fits with the radial neck within the circular annular ligament that attaches the proximal radius to the ulna.
The kinematics of the subtalar joint allows the combined motions of inversionadduction and eversionabduction of the rearfoot Fig. Recall that these motions are components of supination and pronation respectively. Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the proximal radioulnar joint.
Pronation pronation nashun the act of assuming the prone position or the state of being prone. Rotation of the forearm and hand so that the palm faces forward or upward and the radius lies parallel to the ulna. Two principal compound movements occur in this joint.
These movements are affected by several adjacent joints ligaments and periarticular tendinous tissue. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the talocalcaneal joint. The pronation and the supination are movements that take place around a longitudinal axe that pass throughout the elbow and wrist joints connecting both radioulnar joints proximal and distal.
Compensation through Internal rotation pronation and external rotation supination of the shoulder. Describe the arthrokinematics of supination at the proximal radio-ulnar joint lateral rotation of the radial head within the fibro-osseus ring. Pronation and supination can occur at a number of joints but only occurs when the putative axis of motion of a joint is not in any one of the three body planes and makes an angle with all three.
The subtalar joint in the rearfoot is one joint that allows pronation and supination due to the orientation of its putative axis of motion. Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the proximal radioulnar joint. The head of the radius is discoid and fits with the radial neck within the circular annular ligament that attaches the proximal radius to the ulna.
In forearm pronation and supination occur at synovial pivot joints at the proximal and distal ends of radius and ulna. Muscles involved in pronation and supination are attached to radius which then moves around the fixed ulna of forearm. The biceps brachii long head primary movement at the elbow joint include _____ and flexion.
Supination Movement of the forearm away from the shoulder by straightening the elbow to. As the foot is loaded eversion of the subtalar joint dorsiflexion of the ankle and abduction of the forefoot occur. Pronation should not occur past the latter stages of midstance as the regular foot should then supinate in preparation for toe-off.
The normal biomechanics of the foot absorb and direct the occurring throughout the gait whereas the foot is flexible pronation and rigid supination during different phases of the gait cycle. As the foot is loaded eversion of the subtalar joint dorsiflexion of the ankle and abduction of the forefoot occur. Pronation and supination are the triplane motions in the subtalar joint the so-called universal joint of the lower extremity.
In weight bearing pronation occurs at initial contact through the. A physiotherapist explains Pronation and supination as movements that occur at the subtalar joint of the foot. The normal biomechanics of the foot are designed to absorb and direct the forces occurring throughout the gait cycle.
As the foot is loaded eversion of the subtalar joint dorsiflextion of the ankle and abduction of the forefoot occur. Pronation and supination are two types of movements of the foot and hand. Generally they occur at the subtalar joint complex in the foot while in the hand they occur at the proximal radioulnar joint.
Supination vs Pronation. When we are talking about pronation and supination we mostly associate these joint motions with walking gait. Pronation and supination allow the foot to have the dynamic stability required for shock absorption as well as allow for the storing and releasing of kinetic energy through the lower extremities.
The foot is composed of 26 bones and 33 joints so its movement is very complicated. This complexity is very necessary otherwise we cannot adapt to different types of ground cannot bear the weight of several times our body weight.