It is a flattened network of membranous tubules and it continues with the membrane of the nucleus. Schimper was the first to define plastids.
Its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell.
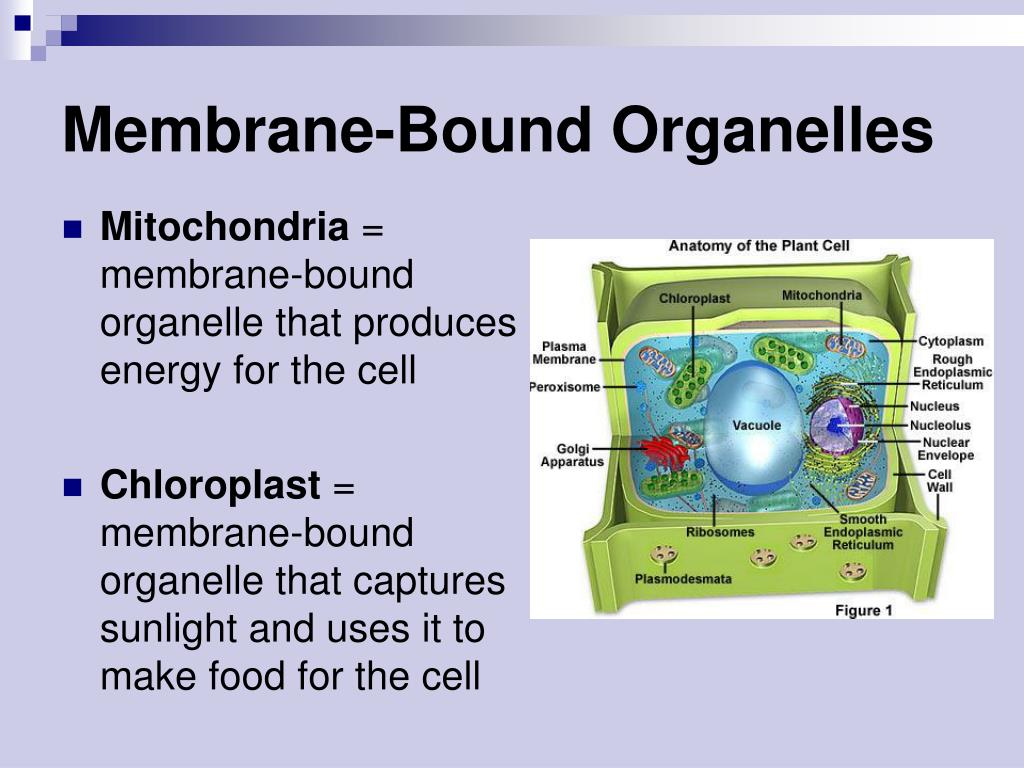
Membrane bound organelle definition. Organelles are structures within a cell that have specific functions. Membrane-bound organelles are organelles protected by a single or double plasma membrane. Mitochondria lysosomes the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus are examples of membrane-bound organelles.
Membrane-bound organelles are one of the defining characteristics of. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles meaning that these organelles eg. Mitochondria lysosome etc are surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer membrane.
This allows organelles within the cells to control what enters and leaves it by using a selectively permeable membrane. A vacuole ˈvækjuːol is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist animal and bacterial cells. The organelle has no basic shape or size.
Its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Membrane-Bound Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells contain many membrane-bound organelles. An organelle is an organized and specialized structure within a living cell.
They are membrane-bound compartments or structures of a cell in general. An organelle by definition is a membrane-bound compartment or structure in a cell that serves a specific purpose. In a broader sense an organelle is any cellular structure that performs a specific function whether or not it is membrane-bound.
These are the so-called membrane bound organelles such as the lysosomes Golgi complex and mitochondria. By the way the similarities between the terms cytoplasm and plasma membrane can help you. Eukaryotic cells contain many membrane-bound organelles.
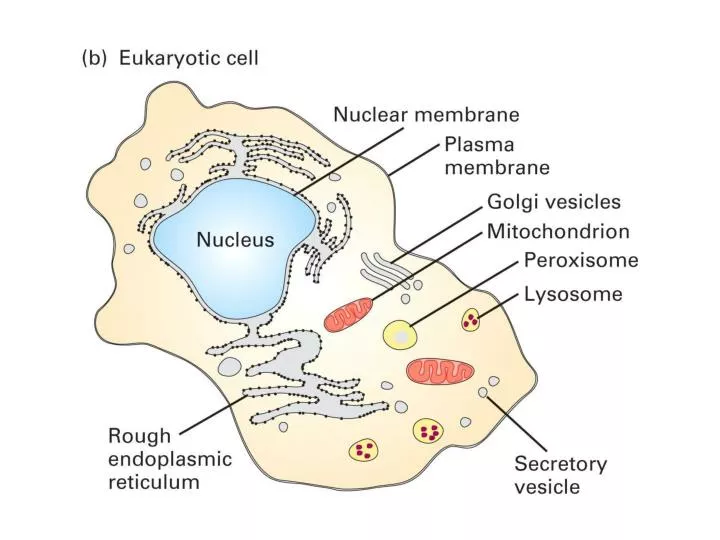
An organelle is an organized and specialized structure within a living cell. The organelles include the nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus vacuoles lysosomes mitochondria and in plants chloroplasts. Membranous organelles are surrounded by single or double membranes defining a boundary to the organelle.
Many of the membranous organelles comprise fluid-filled cavities inside them. Nonmembranous organelles are continuous with the contents in the cytoplasm since they are not surrounded by a membrane. Definition of organelle.
The cellular components responsible for the functioning of a cell are called cell organelles. Different organelles present within the cell are classified into three categories based on the presence or absence of the membrane. Include cell wall ribosomes and cytoskeleton.
A membrane-bound organelle How are organelles shaped. The morphology of most organelles curved is characterized by a combination of flat and membranesuchasintheERFigure1aCellular membranes are lipid bilayers made predominantly of phospholipids and proteins both of which can contribute to membrane curvature. A difference in lipid composition.
What is a nucleus. The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains genetic material DNA of eukaryotic organisms. As such it serves to maintain the integrity of the cell by facilitating transcription and replication processes.
Its the largest organelle inside the cell taking up about a tenth of the entire cell volume. Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition. Endoplasmic reticulum ER is the largest single membrane-bound organelle located in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells.
It is a flattened network of membranous tubules and it continues with the membrane of the nucleus. The membrane-enclosed compartment of the ER is called the ER lumen. Formed molded plural plastids is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants algae and some other eukaryotic organisms.
WikiMatrix Nevertheless the use of organelle to refer to non- membrane bound structures. Plastids are a group of double membrane-bound organelle found in almost all types of cells in plants and algae and also in some other higher organisms. They were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel while A.
Schimper was the first to define plastids. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. These membrane-bound structures are called organelles.
In eukaryotes the cells genetic material or DNA is contained within an organelle called the nucleus where it is.