
Packages and distributes materials such as proteins for. Mitochondria which produce chemical energy.
The cell membrane holds the cell together and allows nutrients into the cell.
Major organelles and their functions. The nucleus is a double-membraned organelle found in all eukaryotic cells. It is the largest organelle which functions as the control centre of the cellular activities and is the storehouse of the cells DNA. By structure the nucleus is dark round surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
What are the functions of the organelles. An organelle is a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell much like an organ does in the body. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei which store genetic information.
Mitochondria which produce chemical energy. And ribosomes which assemble proteins. Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell.
They are involved in many processes for example energy production building proteins and secretions destroying toxins and responding to external signals. Organelles are considered either membranous or non-membranous. Functions of Cell Organelles.
Each cell organelle has a specific role to play in the cells physiology and growth. Since plants are mostly non-motile cell wall presence imparts rigidity capacity to tolerate harsh conditions like wind heat wear and tear etc. It imparts a definite shape to the.
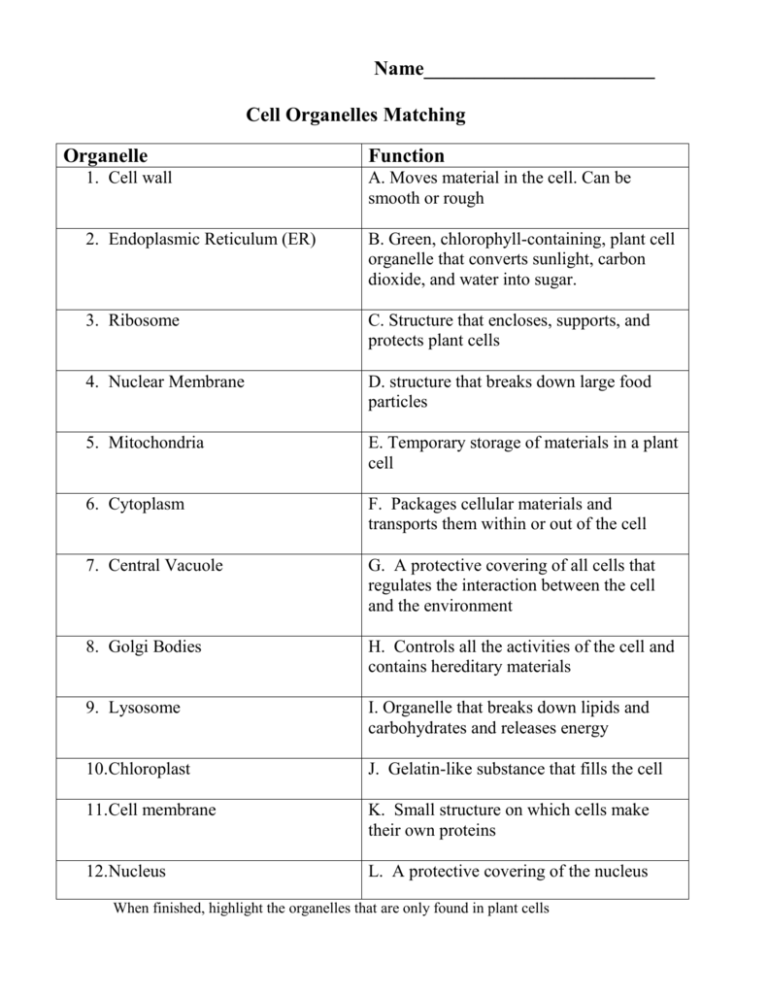
The 13 organelles and their functions are. Nucleus - stores genetic information 2. Ribosomes - makes protein 3.
Plasma membrane - separates the cell from the environment 4. Among the more important cell organelles are the nuclei which store genetic information. Mitochondria which produce chemical energy.
And ribosomes which assemble proteins. ORGANELLE LOCATION DESCRIPTION FUNCTION cell wall plant fungi and bacteria but not animal outer layer rigid strong stiff made of cellulose support grow tall protection allows H2O O2 CO2 to pass into and out of cell cell membrane both plantanimal All cells plant - inside cell wall. ORGANELLES OF THE ANIMAL CELL AND THEIR FUNCTION.
Synthesis of ribosomal RNA. Transport of materials within the cytoplasm. Rough endoplasmic reticulum RER.
Processes packages and distributes proteins to other organelles for export. Cell organelle that houses DNA and directs synthesis of ribosomes and proteins. Oxidizes and breaks down fatty acids and amino acids and detoxifies poisons.
Digestive function in plant cells. Organelles of the plant cell and their function Plasma membrane. Separates the cell from its environment.
Regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell. An organelle found in the cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy photosynthesis. Cytoskeleton Cellular structures that help the cell maintain shape andor move.
Summarize the functions of the major cell organelles. Learn about different cell organelles and their functions including an organelle function chart and illustrations. An organelle think of it as a cells internal organ is a membrane bound structure found within a cell.
Just like cells have membranes to hold everything in these mini-organs are also bound in a double layer of phospholipids to insulate their little compartments within the larger cells. Organelle Main function Structure. Sorting and modification of proteins.
DNA maintenance RNA transcription. Cell Organelles and Their Functions. 31 Cell Membrane The outermost covering of the cell that separates the contents of the cell from its external environment is known as cell membrane.
It is selectively permeable and is made up of bilayer of lipoprotein. The cell membrane holds the cell together and allows nutrients into the cell. Organelles are specialized membrane-bound structures present inside a eukaryotic cell and have specific and precise roles in various cellular processes.
Prokaryotic organisms like bacteria and archaea lack a nucleus and the genetic matter floats freely within the cells. The ribosomes on it makes proteins and move throughout it to the different places in the cell. Does not have ribosomes - acts as a detox unit for foreign substances in the cell.
It is important in the creation and storage of lipids. Packages and distributes materials such as proteins for. The brains of the cell the nucleus directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA.
Make energy out of food. Make process and package proteins. Contains digestive enzymes to help break food down.