
Occipital bone - protects the back of your brain and supports your head. Frontal parietal 2 temporal 2 occipital sphenoid.
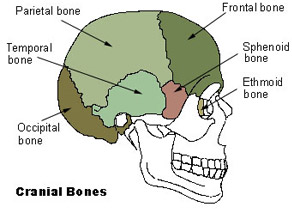
Well go over each of these bones and where theyre located.
List the cranial bones. The 8 cranial bones are the frontal parietal temporal occipital sphenoid and ethmoid bones. Some of these are paired bones. What Are Cranial Bones.
Cranial bone development starts in the early embryo from the neural crest and mesoderm cells. The cranial bones develop by way of intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. Your cranial bones are eight bones that make up your cranium or skull which supports your face and protects your brain.
Well go over each of these bones and where theyre located. 8 cranial bones are. 2 parietal 2 temporal 1 frontal 1 sphenoid 1 ethmoid and 1 occipital.
Occipital bone - protects the back of your brain and supports your head. Temporal bones 2 bones - protect the sides of your brain and support your face. Parietal bones 2 bones - form the.
The cranium is made up of 8 bones. 2 paired parietal bones 2 paired temporal bones frontal bone occipital bone sphenoid bone ethmoid bone The frontal bone is located on the anterior cranium and includes the following features. It makes up the roof of the eye orbits.
Cranium and Facial Bones. The skull consists of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones. The bones are listed in Table but note that only six types of cranial bones and eight types of facial bones are listed because some of the bones as indicated in the table exist as pairs.
The 8 CRANIAL BONES are the FRONTAL bone 2 PARIETAL bones 2 TEMPORAL bones OCCIPITAL bone SPHENOID bone and ETHMOID bone. Together these bones form a kind of bony helmet around the. The human skeleton of an adult consists of around 206 to 213 bones and there are 300 bones in children depending on the counting of sternum which may alternatively be included as the manubrium body of sternum and the xiphoid process.
It is composed of 300 bones at birth but later decreases to 80 bones in the axial skeleton and 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton. Here is the full list. Bones in the Head.
Frontal parietal 2 temporal 2 occipital sphenoid. Ethmoid Facial bones 14. Mandible maxilla 2 palatine 2 zygomatic 2 nasal 2 lacrimal 2 vomer inferior nasal conchae 2 Ear bones 6.
Malleus 2 incus 2 stapes 2 Throat bones 1. Hyoid Bones below the head. The names of the 14 facial bones are.
Inferior nasal concha 2 of them lacrimal bones 2 mandible maxilla 2 nasal bones 2 palatine bones 2 vomer and zygomatic bones or zygoma 2. Parietal 2 Temporal 2 Frontal 1 Occipital 1 Ethmoid 1 Sphenoid 1 Facial Bones. The cranial bones include occipital bone two parietal bones frontal bone two temporal bones sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone.
The top and both sides of the head are formed by the paired parietal bones. Skull bones quiz of the cranial and facial bones for anatomy and physiology. When you are taking anatomy and physiology you will be required to know the location of the cranial and facial bones.
This quiz will test your knowledge on how to identify these. The bones that make up the cranium are called the cranial bones. The remainder of the bones in the skull are the facial bones.
Figure 67 and Figure 68 show all the bones of the skull as they appear from the outside. In Figure 69 some of the bones of the hard palate forming the roof of the mouth are visible because the mandible is not present. The human skull is generally considered to consist of twenty-two boneseight cranial bones and fourteen facial skeleton bones.
In the neurocranium these are the occipital bone two temporal bones two parietal bones the sphenoid ethmoid and frontal bones. Fractures of the cranium typically arise from blunt force or penetrating trauma. When considering cranial fractures one area of clinical importance is the pterion a H-shaped junction between the temporal parietal frontal and sphenoid bones.
The pterion overlies the middle meningeal artery and fractures in this area may injury the vessel. The skull 22 bones is divisible into two parts. 1 the cranium which lodges and protects the brain consists of eight bones Occipital Two Parietals Frontal Two Temporals Sphenoidal Ethmoidal and the skeleton of the face of fourteen Two Nasals Two Maxillae Two Lacrimals Two Zygomatics Two Palatines Two Inferior Nasal Conchae Vomer and Mandible.
The anterior cranial fossa is made up of parts of the frontal ethmoid and sphenoid bones. The middle cranial fossa is made up of parts of the sphenoid temporal and parietal bones. The posterior cranial fossa consists mostly of parts of the occipital and temporal bones and to a smaller extent the sphenoid and parietal bones also.
Either of two irregularly shaped bones that form the back of the hard palate and helps to form the nasal cavity and the floor of the orbits Zygomatic bone the arch of bone beneath the eye that forms the prominence of the cheek. A list of the different bones of the entire axial skeleton can be found on the cancergov website. This reliable source lists a total of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones.
Facial Bones Medical Imaging. Facial bone x-rays give a strictly two-dimensional image. Learn about the anatomy of the skull bones and sutures as seen on CT images of the brain.
The frontal parietal temporal and occipital bones are joined at the cranial sutures. The major sutures are the coronal suture sagittal suture lambdoid suture and squamosal sutures. The cranial sutures are fibrous joints connecting the bones of the skullTo the unknowing individual these shallow grooves may look like fractures.
In fact the intricate windy lines of these thin lines mark the adherence between the bones and the growth and closure of the cranial fontanelles. The dense fibrous tissue that connects the sutures is made mostly out of collagen.