
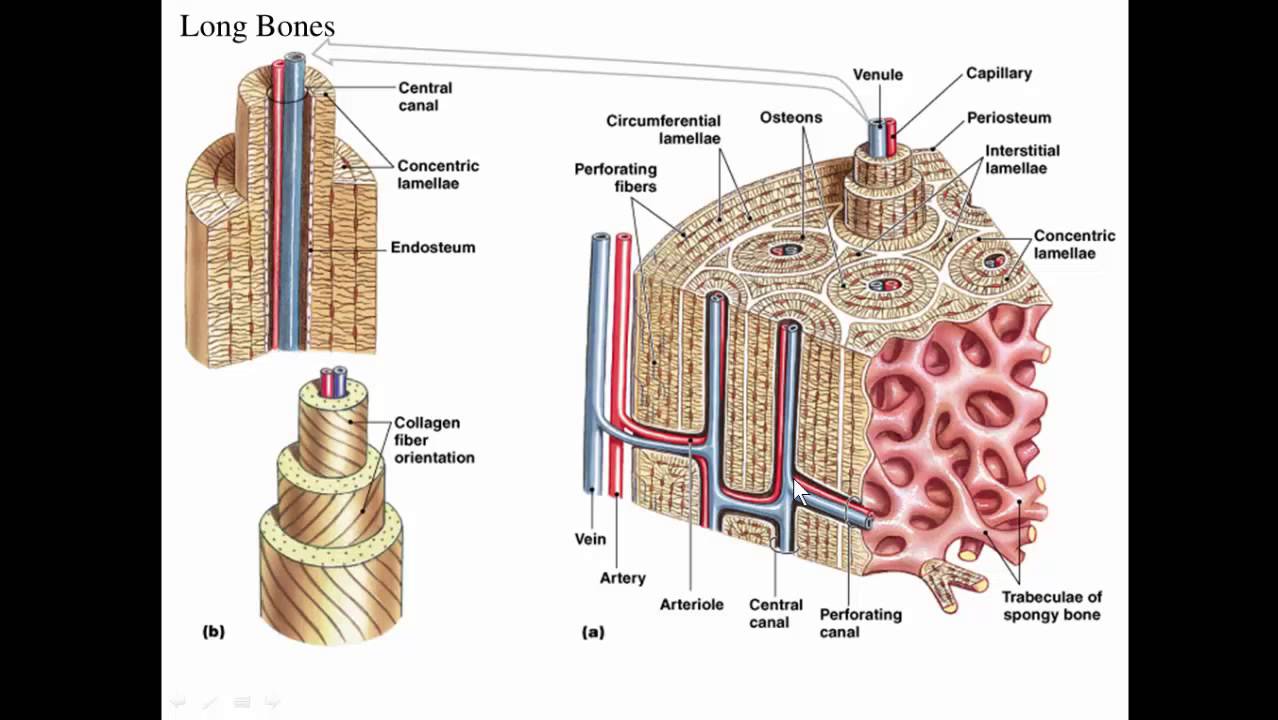
Compact bone is composed of cylindrical units called osteons which are formed from layers of concentric circles called lamellae around a central. The osteon is also known as the Haversian system and is composed of osteocytes.
Blood vessels are located in the hollow center 2.
Functional unit of compact bone. Osteons Functional units of compact bone created by a network of bone cells and blood vessels. Osteocyte A cell which function to maintain and repair bone tissue. Osteoblast Cells which lay down new bone tissue adding the matrix.
Compact bone is composed of cylindrical units called osteons which are formed from layers of concentric circles called lamellae around a central. Compact bone is made of concentric layers of osteocytes and bony matrix. Compact bones provide support to mammalian limbs.
Moreover it is a storehouse of calcium and hosphorus. Compact bone is laid in such a manner that there are histological units seen in. The compact bone is the main structure in the body for support protection and movement.
Due to the strong nature of compact bone compared to spongy bone it is the preferred tissue for strengthSpongy bone is used for more active functions of the bones. The basic units of compact bone are called osteons or Haversian systems. These are cylinder-shaped structures that have a mineral matrix and are home to osteocytes mature bone cells that are trapped in the matrix.
The basic structural and functional unit of compact bone is called the osteon or Haversian System. It is often compared to a bulls-eye target. Spongy bone or trabecular bone is internal to the compact bone and serves as the site of mineral storage and hematopoiesis blood cell production.
The basic functional unit of compact bone is the osteon. The osteon is also known as the Haversian system and is composed of osteocytes. Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy bone also called cancellous bone has open spaces and is supportive but also lightweight and can be readily remodeled to accommodate changing body needs.
Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of osseous tissue Figure 636. It makes up the outer cortex of all bones and is in immediate. Have few osteons or central canals.
Provides strength with little weight. Develop along bones lines of stress. Surfaces of flat bone are composed of.
One of the basic histological differences between compact and spongy bone is that in compact bone the basic functional unit is the osteonHaversian system. Compact bone is usually found where. Stresses arrive from a limited range of directions.
Compact bone is the strong organized hard bone that forms the diaphysis of long bones and is found under the periosteum. It supports the structure and rigidity of the skeletal system. Compact and spongy bone structure Compact bone continued Functional unit is osteon Haversian system continued Canaliculi connect lacunae with each other and central canal Strong along its length 2018 Pearson Education Inc.
The microscopic structural unit of compact bone is called an osteon or Haversian system. Each osteon is composed of concentric rings of calcified matrix called lamellae singular lamella. A An osteon is the functional unit of spongy bone.
B An osteon is the functional unit of compact bone. C An osteon is the structural unit of spongy bone. D An osteon is functional unit of trabecular bone.
E An osteon is the nest that an osteocyte occupies. Compact bone does not have any spaces or hollows in the bone matrix that are visible to the eye. Compact bone forms the thick-walled tube of the shaft or diaphysis of long bones which surrounds the marrow cavity or medullary cavity.
A thin layer of compact bone also covers the epiphyses of long bones. The basic functional unit of compact bone. Made of concentric rings of bone matrix with layers of osteocytes in between.
Blood vessels are located in the hollow center 2. A type of synovial joint. It permits movement in 2 planes.
Flexionextension in the sagittal plane and abductionadduction in the coronal plane. The radio-carpal wrist joint. The functional units of compact bone are osteons.
Which contain a centrally located Haversian canal encased in lamellae concentric rings. Osteocytes can be observed in the lacunae between the osteons. The osteons unlike the trabeculae are densely packed making compact bone tougher and heavier than spongy bone.
Found where strength is of great importance like the shaft of long bones and the perimeter of all bones. Is comprised of repeating microscopic and functional units called Haversian systems or Osteons. Compact bone also called cortical bone dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic ground substance and inorganic salts leaving only tiny spaces lacunae that contain the osteocytes or bone cellsCompact bone makes up 80 percent of the human skeleton.
The remainder is cancellous bone which has a spongelike appearance with numerous large spaces and is found in the. A vertical growth of bones being dependent on age B the modification of bone due to intermittent growth spurts during adolescence C diameter of the bone being dependent on the ratio of osteoblasts to osteoclasts D the function of bone being dependent on shape E the thickness and shape of a bone being dependent on stresses placed upon it the. Compact bone forms the outer shell of bone.
In this type of bone the lamellae are organised into concentric circles which surround a vertical Haversian canal which transmits small neurovascular and lymphatic vessels. This entire structure is called an osteon and is the functional unit of bone.