Os ethmoidale is an unpaired bone of the skull that contributes to the medial wall of the orbit the nasal cavity and the nasal septum. Removes and traps pathogens and particulate matter from the inspired air.

The inner surface is grooved by the passage of the nasociliary nerve.
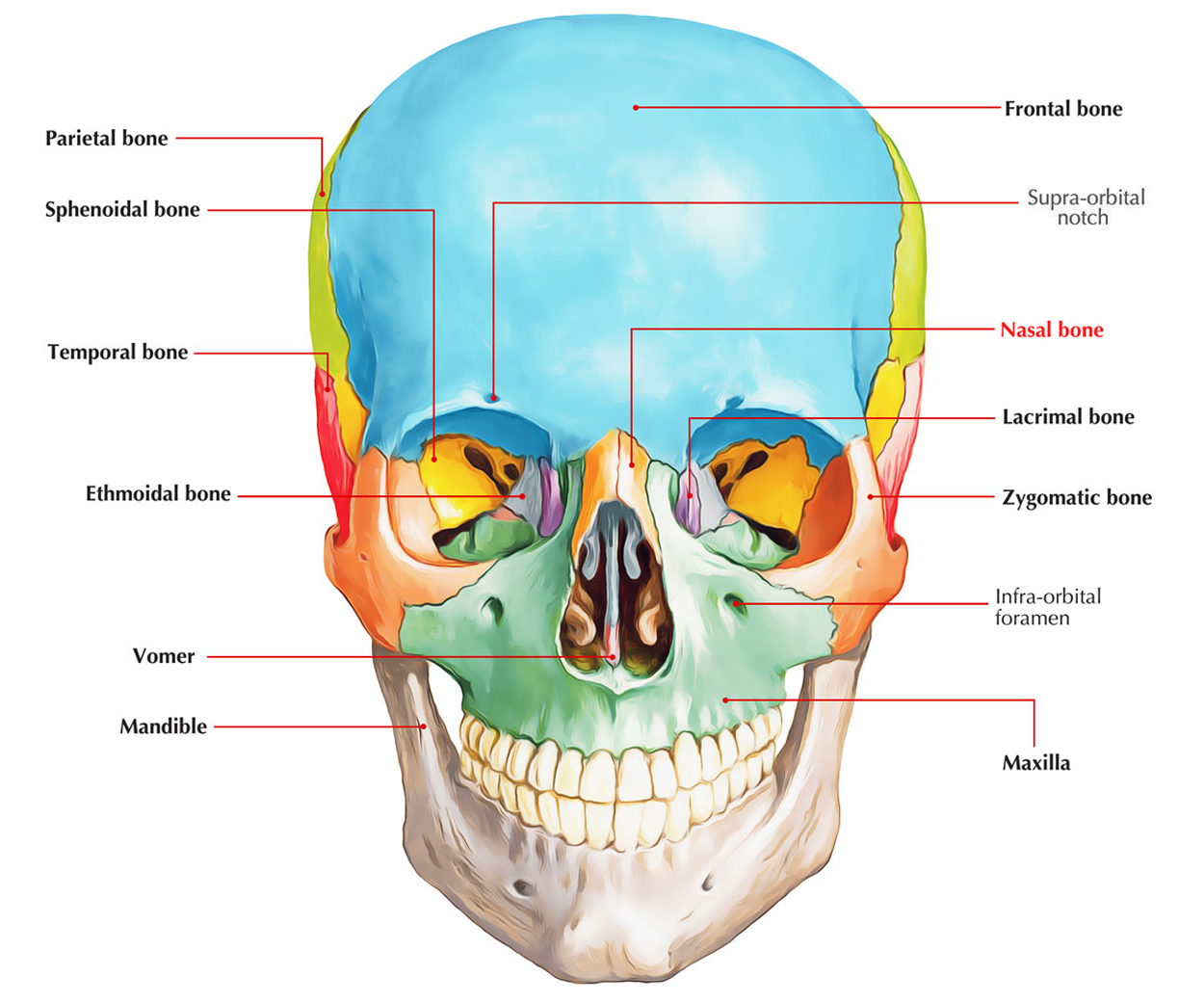
Function of the nasal bone. The function of each nasal bone is to bind together the cartilage that forms individual nose contours and shapes. Each nasal bone has four bones which. The nasal bones are ossified intramembranously via the cartilaginous nasal capsule.
Clinically the hypoplasia or absence of nasal bones is a common feature in Down syndrome trisomy 21 and other chromosomal abnormalities. That is why the detection of the nasal tip during ultrasound has become part of prenatal screening tests in many countries. The human body contains eight facial bones which are necessary to protect the brain sense organs sight smell taste and act as the base for soft tissue formation.
Learn about the bones. The prominent bone within the nasal chamber is called the nasal bone. This bone actually creates the peak of the nose while cartilage covers the tip.
What is nasal bone fx-closed. Unlike many other facial bones nasal bones do not have a broad range of functions or anatomical structures. They are primarily structural.
A nasal bone x-ray shows this bone form but is not a good indicator of bone density or internal surface posterior shape. The uppermost part is thicker than the bottom. The inner wall is concave.
Nasal Bone 2 The nasal bone is one of two small bones that articulate join with each other to form the bony base bridge of the nose. They also support the. Both the superior and middle nasal conchae project from parts of the ethmoidal labyrinth part of the ethmoid bone 15 while the inferior nasal concha is an individual bony structure 16.
They contribute to divide the breathing space within the cavity into the tree meatuses and allow the inhaled air to better interact with the different parts of the cavity 3. Nasal bone - Anatomy Function Diagram - Human Anatomy Kenhub - YouTube. This video looks at the nasal bones.
Two small bones found centrally in the superior facial skeleton. It consists of nasal skeleton which houses the nasal cavity. The nasal cavity has four functions.
Warms and humidifies the inspired air. Removes and traps pathogens and particulate matter from the inspired air. Responsible for sense of smell.
Concerns of Function and Feature The nose is the most common facial bone to sustain a fracture. Such injuries may result in deformities affecting the outside and inside structures of the nose which can cause problems breathing sinus infections nose bleeds snoring nasal obstruction and distorted facial features. The nasal bone which makes up the bridge of your nose.
The bones that hold your dental alveoli or tooth sockets. The bony part of your nasal septum. The maxilla has several main functions.
This is ironic because one of the functions of this bone marking is to _____. Separate the left and right halves of the nasal cavity b. Attach to the dura matter holding the brain in place c.
Attach to and support the hyoid bone d. Anchor important chewing muscles. The function of each nasal bone is to bind together the cartilage that forms individual nose contours and shapes.
Each nasal bone has four bones which form joints. Two cranium and two facial bones. The cranium bones are called the ethmoid and frontal.
The facial bones have many functions as each individual bone supports different areas of the face. Firstly the facial bones protect the soft tissues that lie underneath such as the mucous membranes and sensory cells of the nasal cavity the oral cavity the eyes and if the ethmoid is included the pituitary gland of the brain. The function of the paranasal sinuses is a topic of much debate.
Various roles have been suggested. Lightening the weight of the head. Supporting immune defence of the nasal cavity.
Increasing resonance of the voice. The paranasal sinuses are formed during development by the nasal cavity eroding into the surrounding bones. All the sinuses therefore drain.
Each nasal cavity has a lateral wall medial wall roof and floor. The cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone forms the roof of the nasal cavity the ethmoid bone is the part of the cranial base where the fibers of the olfactory nerve pass through which borders above with the nasal bone and the body of. The paired nasal bones form the bridge of the nose and with the frontal process of the maxilla laterally and the nasal process of the frontal bone superiorly.
The inner surface is grooved by the passage of the nasociliary nerve. The nasal cavity functions to allow air to enter the respiratory system upon respiration. Structures within the cavity regulate the flow of air and particles it contains.
The olfactory region of the nasal cavity regulates the sense of smell. The ethmoid bone also ethmoidal bone ethmoid latin. Os ethmoidale is an unpaired bone of the skull that contributes to the medial wall of the orbit the nasal cavity and the nasal septum.
The ethmoid bone includes the cribriform plate with openings that transmit the olfactory nerves CN I and it also houses paranasal sinuses called the ethmoidal air cells.