
Which of the following is not a function of theGlenoid Labrum. It coats the surface of the socket area with a soft cartilage enabling the shoulder to move more freely and painlessly.
Labrum FunctionBiomechanics.
Function of glenoid labrum. Describing glenoid cavity with labrum its dimensions and depth using digital caliber then remove the labrum is measured again the major axis of the articular cavity depth and the index with. Describing glenoid cavity with labrum its dimensions and depth using digital caliber then remove the labrum is measured again the major axis of the articular cavity depth and the index with glenohumeral labrum and without the same. 1With labrum front-back max 3278 min 2609.
Upper- lower max 4406 min 3369. We used 10 cadaveric shoulders injected with 10 formalin we practice macroscopic dissection. Describing glenoid cavity with labrum its dimensions and depth using digital caliber then remove the labrum is measured again the major axis of the articular cavity depth and the index with glenohumeral labrum and without the same.
Which of the following is not a function of theGlenoid Labrum. Increases the compression and contact forces at the shoulder by generating forces drawing the humeral head into the glenoid fossa. Increase the width and depth of the articulating space Account for 20 of the passive stability in compressive motions Increases contact area up to 75.
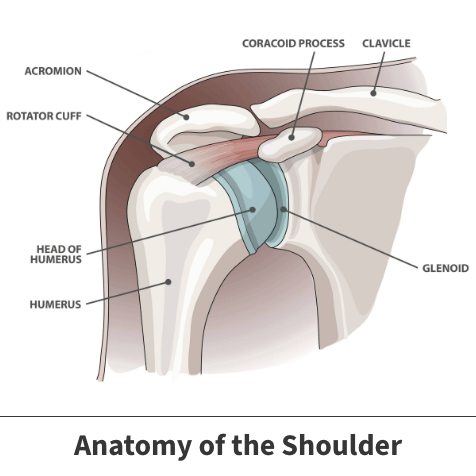
In anatomy and physiology the term labrum is used to refer to an edge or a brim. The labrum surrounding the shoulder socket is called the the glenoid labrum. It coats the surface of the socket area with a soft cartilage enabling the shoulder to move more freely and painlessly.
The glenoid labrum also called the glenoidal labrum describes a ring of flexible cartilage that lines the cavity of the shoulder joint. Its purpose is to increase the depth of the shoulder cavity and add overall stability to the shoulder joint. The glenoid labrum is a fibrous ring that helps hold the upperarm bone humerus in the glenoid fossa.
A shallow socket in theshoulder blade scapula. Functions Of The Glenoid Labrum Homeworkcre. The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity that serves to deepen the cavity.
The glenoid fossa of the scapula is relatively shallow contacting at most only a third of the head of the humerus. The glenoid labrum is an integral component of the glenohumeral capsules insertion into the glenoid and changes in labrum geometry and mechanical properties may lead to the development of glenohumeral joint pathology. The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure that runs circumferentiallyaround the rim of the glenoid fossa116 It provides stability to the glenohumeral joint by contributing approximately 50 of the depth of the glenoid and is an attachment site for the glenohumeral ligaments anteriorly and the long head of the biceps.
Glenohumeral ligament is the glenoid labrum a vascularized ring of fibrous tissue extending distally from the glenoid 2026. The labrum provides an increased depth and concavity to the glenoid fossa for resistance to humeral head translation 2122. Addition-ally the labrum serves as a transition zone between the deform-.
The glenoid labrum is a wedge-shaped ring of fibrocartilage that encircles the bony glenoid deepening the glenoid cavity and serving to bridge bone to the glenohumeral ligaments and biceps tendon Fig 2-13. The glenoid labrum is a fibrous ring of tissue which attaches to the rim of the glenoid which is the shallow depression of the scapula or shoulder blade where the ball of the humerus sits. The glenoid labrum increases the depth of the shoulder cavity making the shoulder joint more stable.
Labrum FunctionBiomechanics. The glenoid labrum acts as a passive stabilizer to the glenohumeral articulation by adding depth to the shallow glenoid fossa. It also serves as a primary attachment site for the GHLs joint capsule and long head of the biceps tendon.
The knee meniscus and glenoid labrum are anatomically distinct yet analogous structures. Although the gross anatomy differs both tissues are composed of fibrocartilage with a complex but well-organized collagen microstructure. The meniscus and labrum function to increase congruity and stability decrease contact stresses and.
A SLAP lesion superior labrum anterior front to posterior back is a tear of the rim above the middle of the socket that may also involve the biceps tendon. A tear of the rim below the middle of the glenoid socket that also involves the inferior glenohumeral ligament is called a Bankart lesion. The glenoid labrum is essential for the structure and therefore the function of the glenohumeral joint.
This joint has the greatest range of motion of any articulation in the bodythe cost of which is vulnerability to injury in the form of instability. Normal labrum anatomy and biomechanics21. The glenoid labrum is the fibrocartilage of the shoulder joint.
It comprises 3 sides and 1 edge. The superficial side is free and responsive to the humeral head. The articular side adheres to a greater or lesser degree according to area to the edge of the glenoid cavity.
And the peripheral side is in continuity with the joint capsule. The labrum is responsible for the shoulder being stable despite the amount of load that is being pout on it on a daily basis. Because of this load and repetitive strain that is being put on the labrum at times it causes this labrum to tear.
This is what is termed as a Glenoid Labrum Tear.