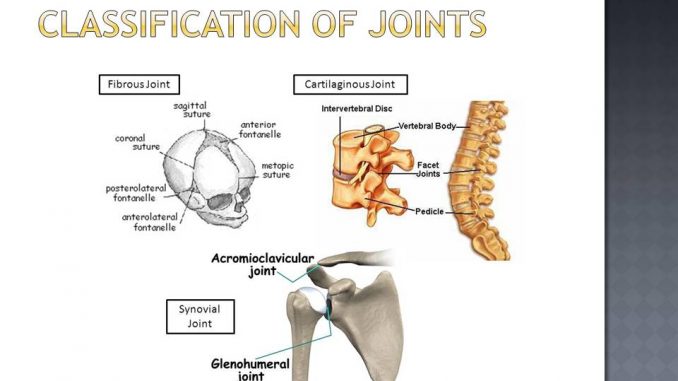
In cartilaginous joints the b ones are united by cartilage. Cartilage is the fibrous elastic tissue that cushions joints and provides organ structures.

This type of joint allows for limited movement.
Function of cartilaginous joints. A joint has two main functions. To allow mobility of the skeletal system and to provide a protective enclosure for vital organs. Thereof which is a function of cartilaginous tissue.
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in many parts of the body. Cartilaginous joints also forms the growth regions of immature long bones and the intervertebral discs of the spinal column. What are the main functions of the disc.
The discs throughout the spine have three primary functions. They act as a shock absorbers in the spine positioned between each bony vertebra. They act as tough ligaments that hold the vertebrae of the spine together.
The function of cartilaginous joints is to bind bones together in a more rigid and stable structure than synovial joints while still allowing a small degree of flexibility. This flexibility allows. A cartilaginous joint is a connection between two bones where the connecting tissue is cartilage.
The type of cartilage connecting the bones differs such that two different types of. A cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage is called a symphysis growing together. Fibrocartilage contains numerous bundles of thick collagen fibers thus giving it a much greater ability to resist pulling and bending forces when compared with hyaline cartilage.
Each disc forms a cartilaginous joint to allow slight movement of the vertebrae and acts as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together. The discs consist of an outer annulus fibrosus that surrounds the inner nucleus pulposus. The annulus fibrosus and the nucleus.
Functions of the cartilaginous joints. Depending on where they are located the cartilaginous joints fulfill different functions in the body. Among the most important are.
Their function as sites of contact or union between different bones of the body allowing certain ranges of mobility that are very important for the stability of the skeleton. At cartilaginous joints bones are united by hyaline cartilage to form a synchondrosis or by fibrocartilage to form a symphysis. A The hyaline cartilage of the epiphyseal plate growth plate forms a synchondrosis that unites the shaft diaphysis and end epiphysis of a long bone and allows the bone to.
The vertebrae are examples of cartilaginous joints. Most of the joints in the body are synovial joints. These joints are freely movable and are characterised by being surrounded by an articular capsule which contains the synovial fluid.
Lubricates the joints Supplies nutrients to the cartilage and. -cartilaginous joint connected via hyaline cartilage. Epiphyseal growth plate-functionally the epiphyseal plate is synarthrosis.
-when bone elongation stops and bone replaces hyaline cartilage the function is now synostosis a bony joint. Cartilage is the fibrous elastic tissue that cushions joints and provides organ structures. Cartilage is a connective tissue type one of 6 major types that is an essential part of many of the structures in the body.
Cartilage is stiffer and less flexible than muscle but not as rigid or hard as bone. Cartilage provides shape to some parts of. A joint usually refers to a point where two or more joints meet each other.
In simple words it is a type of connection that is formed between two different bones in the skeletal system. In both animals and humans joints function by providing the framework which allows movement and is also involved in providing strength and. The function of the cartilaginous joints is to give a little more flexibility between the bones which generates slight movements however this movement is not as free as the synovial joint.
Likewise it acts as shock absorber since it has elastic resistance to pressure due to high mechanical loads. In a cartilaginous joint the bones are united by fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage. There are two main types.
Synchondroses primary cartilaginous and symphyses secondary cartilaginous. In a synchondrosis the bones are connected by hyaline cartilage. These joints are immovable synarthrosis.
A cartilaginous joint is an anatomical structure within the body where two bones connect and which is made of cartilage. This type of joint allows for limited movement. The structure and mobility of these mechanisms make them distinct from the two other types of joints.
Two types of cartilaginous joints include primary. In cartilaginous joints the b ones are united by cartilage. They are slightly movable joints and l ack a joint cavity.
There are two types of cartilaginous joints. 1Primary cartilaginous joint Synchondrosis The articulating bones are connected via hyaline cartilage. The joints are immovable and temporary in nature ie.
After certain age the. Cartilaginous joints are partly movable joints comprising of symphysis or synchondrosis joints. These joints occur only in those regions where the connection between the articulating bones is made up of cartilage.
Synchondrosis are temporary cartilaginous joints which are present in young children and last until the end of their puberty. Joints that unite bones with cartilage are called cartilaginous joints. There are two types of cartilaginous joints.
1 A synchrondosis is an immovable cartilaginous joint. One example is the joint between the first pair of ribs and the sternum. Cartilaginous joints are a type of joint where the bones are entirely joined by cartilage either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage.
These joints generally allow more movement than fibrous joints but less movement than synovial joints. Primary cartilaginous joint These cartilaginous joints are composed entirely of hyaline cartilage and are known as synchondroses. Fibrocartilaginous lip that extends from the edge of a joint socket ball and socket joints labrum function helps deepen the socket and increase the area of contact between the ball-like surface of the head of the humerus or femur.
Similarly at a cartilaginous joint the adjacent bones are united by cartilage. In contrast at a synovial joint the articulating bone surfaces are not directly united to each other but come together within a fluid-filled joint cavity. The functional classification of body joints is based on the degree of movement found at each joint.
Joints and their function. A joint is where two or more bones meet. The hip is a typical synovial joint.
All synovial joints have the same components. Cartilage reduces friction.