Prokaryotes are small single cell organisms usually less than a micrometer abbreviated µm. Eukaryotic Cells Definition.

Outer layers of cell.
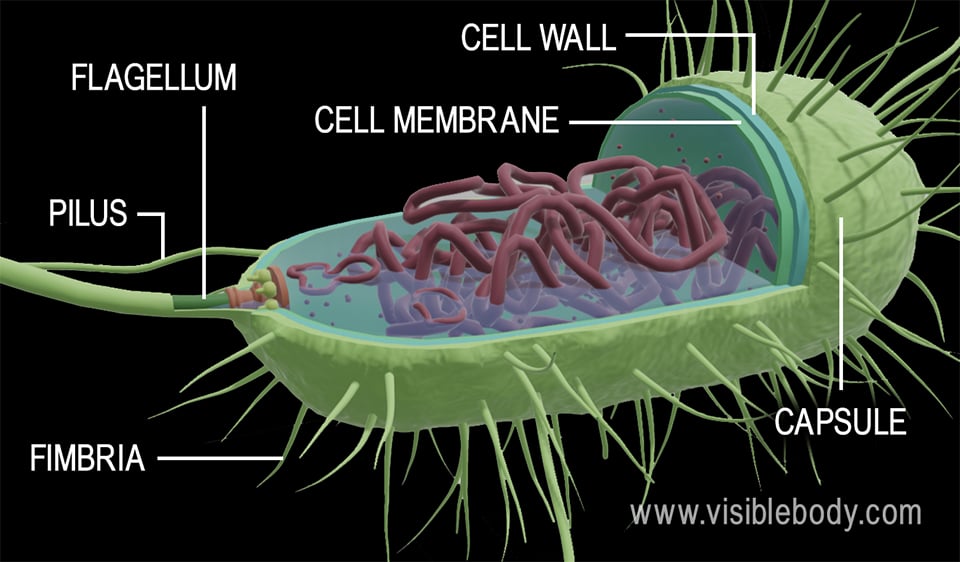
Features of prokaryotic cell. The cell wall of a prokaryote acts as an extra layer of protection helps maintain cell shape and prevents dehydration. Prokaryotic cell size ranges from 01 to 50 μm in diameter. The small size of prokaryotes allows quick entry and diffusion of ions and molecules to other parts of the cell while also allowing fast removal of waste products out of the cell.
Prokaryotic cells have different characteristic features. The characteristics of the prokaryotic cells are mentioned below. They lack a nuclear membrane.
Mitochondria Golgi bodies chloroplast and lysosomes are absent. The genetic material is present on a single chromosome. Prokaryotic cells are not as complex as eukaryotic cells.
They have no true nucleus as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell but is coiled up in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell shapes. The most common bacteria shapes are spherical rod-shaped and.
Features of Prokaryotic cell. Prokaryotic cells are very small in size 01-03 μm. The cell is formed of peptidoglycan like Bacteria Blue-green algae.
Some of the most important characteristics of prokaryotic cells are as follows. The prokaryotic Gr pro-primitive karyon-nucleus cells are the most primitive cells from morphological point of view. They occur in bacteria and blue green algae.
Prokaryotes are small single cell organisms usually less than a micrometer abbreviated µm. 1000 µm1 millimeter abbreviated mm are generally not longer than Зµm. The cell wall of a prokaryote acts as an extra layer of protection helps maintain cell shape and prevents dehydration.
Prokaryotic cell size ranges from 01 to 50 μm in diameter. The small size of prokaryotes allows quick entry and diffusion of ions and molecules to other parts of the cell while also allowing fast removal of waste products out of the cell. Feature Eukaryotic cell Prokaryotic cell.
Most are 5 μm - 100 μm. Most are 02 μm - 20 μm. Outer layers of cell.
Cell membrane surrounded by cell wall in plants and fungi. All prokaryotic cell shares four common components-1. Plasma membrane It refers to the outer membrane which separates the inner environment from the external environmentIt is a thin lipid bilayer.
It is selectively permeable. ProkaryotesArrangements of Cells Bacteria sometimes occur in groups rather than singly. Bacilli divide along a single axis seen in pairs or chains.
Cocci divide on one or more planes producing cells in. - pairs diplococci - chains streptococci - packets sarcinae - clusters staphylococci. Size shape and arrangement of cells.
Features of Prokaryotic Cells. The genetic material is localised in a region known as nucleoid and it has no surrounding membrane. These cells contain large numbers of the ribosome for protein synthesis.
In some prokaryotes the cell membrane folds to form structures known as. Prokaryotic cell characteristics Feature of Prokaryotes. Among the main feature of prokaryotic cells we can highlight the following.
Their diet can be autotrophic they make their own food or heterotrophic they eat other peoples food. Like eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm a gel-like substance that makes up the filling of the cell and a cytoskeleton that holds components of the cell in place. Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes which are organelles that produce proteins and vacuoles small spaces in cells that store nutrients and help eliminate waste.
Prokaryotic are cells that lack a nucleus nuclear membrane. Prokarotic cells are single cells but are subdivided into Bacteria and Arachaea as mention in the previous slide. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus nuclear membrane.
Plants animals fungi and protists a. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the only kinds of cells that exist on Earth. Prokaryotes are mostly unicellular organisms that lack nuclei and membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotes include larger more complex organisms such as plants and animals. Most are 5 μm 100 μm. Most are 02 μm 20 μm.
Outer layers of cell. Cell membrane - surrounded by cell wall in plants and fungi. Cell membrane - surrounded by.
The defining characteristic feature that distinguishes between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells the true nucleus is absent moreover membrane-bound organelles are present only in eukaryotic cells. Other major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are that prokaryotic cells are exclusively unicellular while the same does not apply to eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells in that they lack any membrane-bound organelles including a nucleus. Instead prokaryotic cells simply have an outer plasma membrane DNA nucleoid structure and ribosomes. Which feature is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
The three main features of a prokaryotic cell We have its insides. Cytoplasm is where its organelles are suspended. These ribosomes facilitate in manufacturing the cells proteins used in many cellular activities.
It is a tiny DNA molecule. The genophore of a prokaryotic cell where its. Eukaryotic Cells Definition.
A cell has a well-developed nucleus and membrane-bounded cell structure or organelles called a eukaryotic cell. This cell is also called a modern cell. It has a more and well-developed function as compared to the prokaryotic cell.
Animals plants fungi and Protists are eukaryotic cells and organisms. They have a well-developed structure and more functions.