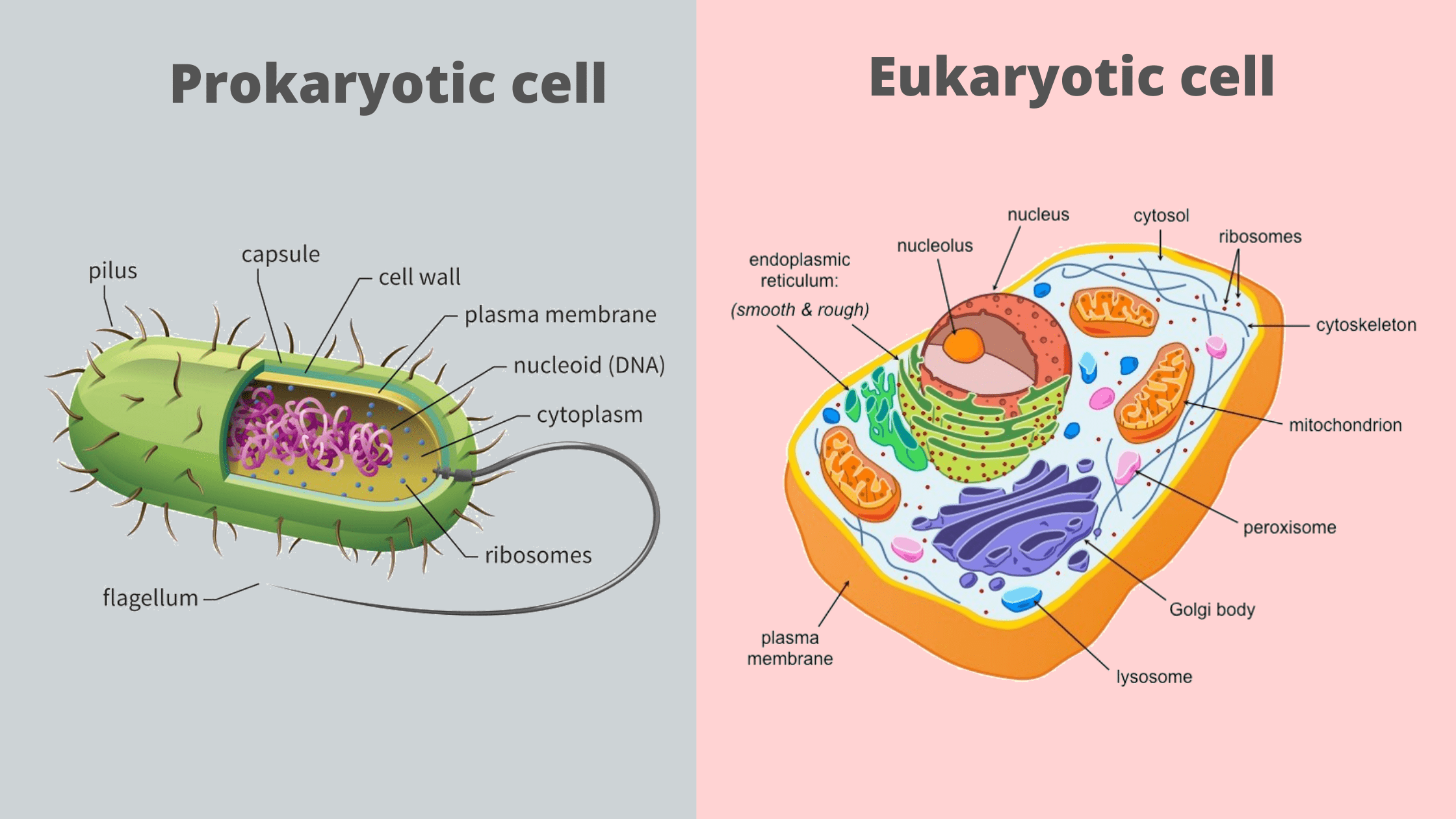
The Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles are called Prokaryotic Cells. A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells.

Examples of Eukaryotic Cells.
Examples of eukaryotic cell. Examples of Eukaryotic Cells. Animals such as cats and dogs have eukaryotic cells. Plants such as apple trees have eukaryotic cells.
Fungi such as mushrooms have eukaryotic cells. Protists such as amoeba and paramecium have eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are defined as cells containing organized nucleus and organelles which are enveloped by membrane-bound organelles.
Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants animals protists fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Examples of Eukaryotic Cells.
Animals such as cats and dogs have eukaryotic cells. Plants such as apple trees have eukaryotic cells. Fungi such as mushrooms have eukaryotic cells.
Protists such as amoeba and paramecium have eukaryotic cells. Insects have eukaryotic cells. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell.
A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells. The cells divide by a process called mitosis. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure.
The nucleus contains a single linear DNA which carries all the genetic information. Examples of Eukaryotic Cells Based on the types of organisms eukaryotic cells are of four types. 1 plant cells 2 animal cells 3 fungal cells and 4 protozoa.
Eukaryotic cells are those who contains nucleus as well as the organelles. Example of prokaryotes are Archaea and Eubacteria. Eukaryotic organism examples are.
They also have relatively large cells generally much larger than bacterial cells. All protists fungi plants and animals are examples of eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are cells with a membrane bound nucleus.
They also have other membrane bound cell organelles. Examples of Prokaryotic cells are. Bacteria and blue-green algae.
Yeasts Fungi Animal cells including Protozoa and Plant cells including Algae. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus which means the cells DNA is surrounded by a membrane. Therefore the nucleus houses the cells DNA and directs the synthesis of proteins and ribosomes the cellular organelles responsible for protein example of eukaryotes which.
Examples of eukaryotic cells. Examples of prokaryotic cells. Answer 1 of 8.
You are an eukaryotic organism because your cells exhibit compartmentalization - they have a membrane-enclosed nucleus and organelles functioning by division of labour within the cell. It is a unicellular cell. It can be unicellular or multicellular.
It lacks a well-defined nucleus. It has a well-defined nucleus. Bacterial cell Cyanobacteria etc.
Plant cell animal cell etc. Just about every organism youre familiar with is a eukaryote. Single celled organisms like yeast paramecia and amoebae are all eukaryotes.
Grass potatoes and pine trees. A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells. The cells divide by a process called mitosis.
The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure. The nucleus contains a single linear DNA which carries all the genetic information. Examples of Eukaryotic Cell.
The examples of eukaryotic cells are mentioned below. Eukaryotic cells are typically much larger than those of prokaryotes having a volume of around 10000 times greater than the prokaryotic cell. They have a variety of internal membrane-bound structures called organelles and a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules microfilaments and intermediate filaments which play an important role in defining the cells organization and shape.
Answer 1 of 11. Prokaryotic cell lacks a membrane-bound nucleus mitochondria or any other membrane-bound organelle. In prokaryotic cell all the intracellular components such as DNA RNA proteins and metabolites are located together in the cytoplasm rather than in separate cellular compart.
Eukaryotic cells also contain mitochondria which are responsible for the creation of energy which is then utilized by the cell. Present in only plant cells chloroplasts are the subcellular sites of photosynthesis. Examples of eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells Figure 142 are considered simple cells for three reasons. The Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles are called Prokaryotic Cells.