A compact bone example would be the significant cortical bones of all long bones such as those on arms and legs. Irregular bones do not fit into the above categories.
Almost 80 or above weight of human skeleton is contributed by compact bones.
Examples of compact bone. The femur is an example of a long compact bone. Major functions of compact bones within the body include support and protection because the tissue is so hard. In general the skeletal system also stores minerals produces blood cells and stores chemical energy.
Animals have compact bones located within their bodies as well though the structure of their skeletal system and the number of bones are often. They have only a thin layer of compact bone tissue. Examples of short bones include those of the wrist and ankle.
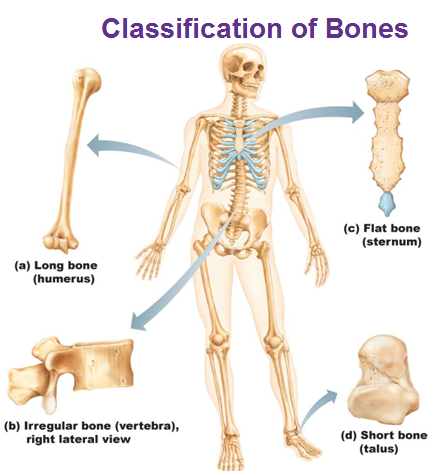
The bones of the human skeleton can be grouped into five types. Long short flat irregular and sesamoid. Flat bones often have two thin parallel layers of compact bone with spongy bone inside.
Cancellous Bone The softer less dense tissue that makes up the ends of bones and creates blood cells. Osteons Functional units of compact bone created by a network of bone cells and blood vessels. Osteocyte A cell which function to maintain and repair bone tissue.
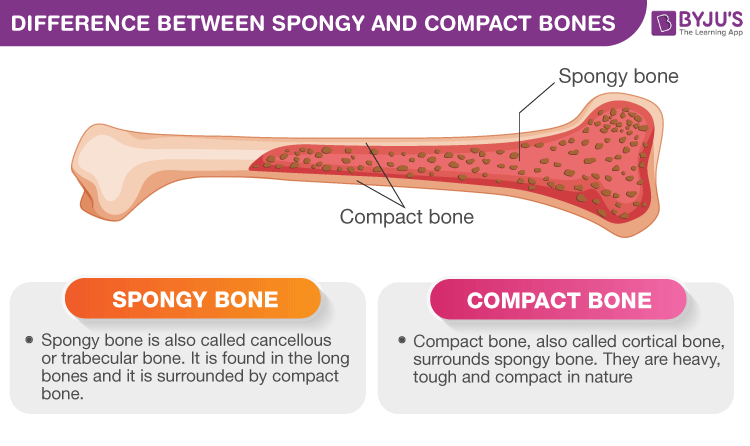
Compact bone also called cortical bone dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic ground substance and inorganic salts leaving only tiny spaces lacunae that contain the osteocytes or bone cells. Compact bone makes up 80 percent of the human skeleton. The remainder is cancellous bone which has a spongelike appearance with numerous large spaces and is found in the marrow space medullary cavity of a bone.
Both types are found in most bones. Spongy bone gets its name because you guessed it it looks like a sponge and has many porous spaces whereas compact bone is dense appearing as if it were compacted together. Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy bone also called cancellous bone has open spaces and is supportive but also lightweight and can be readily remodeled to accommodate changing body needs.
Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of osseous tissue Figure 636. It makes up the outer cortex of all bones and is in immediate. The differences between compact and spongy bone are best explored via their histology.
Most bones contain compact and spongy osseous tissue but their distribution and concentration vary based on the bones overall function. Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy cancellous bone has open spaces and supports shifts in weight distribution. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of bone.
You find cancellous bone in a number of places. The medullary cavity of long bones. And inside short flat as pictured above and irregular bones.
Long bone examples are the femur tibia and humerus. The bones of the skull are flat as well as the sternum. The periosteum forms the outer surface of bone and the endosteum lines the medullary cavity.
Flat bones like those of the cranium consist of a layer of diploë spongy bone lined on either side by a layer of compact bone Figure 69. In compact bone the haversian systems are packed tightly together to form what appears to be a solid mass. The osteonic canals contain blood vessels that are parallel to the long axis of the bone.
These blood vessels interconnect by way of perforating canals with vessels on the surface of the bone. Made up of osteons. Made up of trabeculae.
Calcium is present in high quantity in them. Very small amount of calcium is present in them. Almost 80 or above weight of human skeleton is contributed by compact bones.
The rest 20 weight of the skeleton is contributed by spongy bones. These bones are cylindrical in shape. The sternum is composed of highly vascular tissue covered by a thin layer of compact bone which is thickest in the manubrium between the articular facets for the clavicles.
Additionally the outer shell of the long bone is compact bone then a deeper layer of cancellous bone spongy bone which contains in the medullary cavity the bone marrow. Compact bone separated by cancellous or spongy bone. Examples include the sternum ribs scapula and certain skull bones.
These are complex and irregu-larly shaped bones. Examples include the verte-brae and certain facial bones. Sesamoid bones are small bones embedded in a tendon and resemble the shape.
Flat bones like those of the cranium consist of a layer of diploë spongy bone lined on either side by a layer of compact bone. The two layers of compact bone and the interior spongy bone work together to protect the internal organs. These are bones in the body which do not fall into any other category due to their non-uniform shape.
Good examples of these are the Vertebrae Sacrum and Mandible lower jaw. They primarily consist of cancellous bone with a thin outer layer of compact bone. 1 Thin bony plates in spongy bone 2 Round hollow cylinders in compact bone 3 Transverse tunnels containing blood vessels and nerves 4 Small spaces in bone occupied by osteocytes.
A compact bone example would be the significant cortical bones of all long bones such as those on arms and legs. They are hard and contain yellow bone marrow. These cylindrical bones constitute 80 of the skeletal systems weight.
It is highly vascularized and contains red bone marrow. Spongy bone is usually located at the ends of the long bones the epiphyses with the harder compact bone surrounding it. It is also found inside the vertebrae in the ribs in the skull and in the bones of the joints.
Spongy bone is softer and weaker than compact bone but is also more flexible. Since they act to hold the tendon further away from the joint the angle of the tendon is increased and thus the leverage of the muscle is increased. Examples of sesamoid bones are the patella and the pisiform.
Irregular bones do not fit into the above categories. They consist of thin layers of compact bone surrounding a spongy interior. Compact bone also known as cortical bone makes up the outside portion of bones.
This tissue is very closely packed to make it really solid and hard.