
Cartilaginous joints allow more movement between bones than a fibrous joint but less than the highly mobile synovial joint. These joints here allow for only a little movement such as in the spine or ribs.
Primary cartilaginous joints synchondroses.
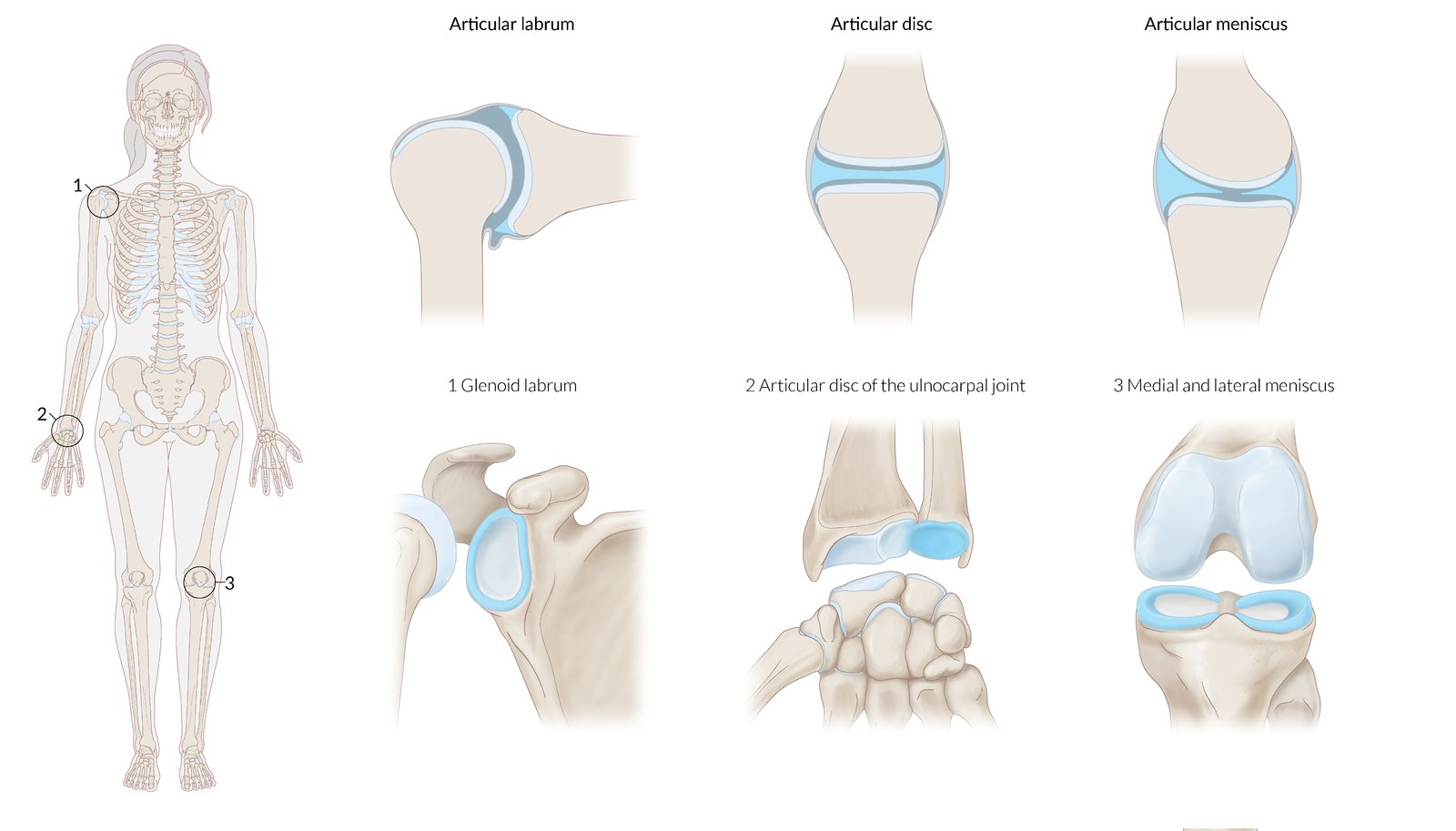
Examples of cartilaginous joints. Cartilaginous joints are connections between bones that are held tightly together by cartilage - specifically either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage. Many Graphics of them are here. One example is the first sternocostal joint where the first rib is anchored to the manubrium by its costal cartilage.
The articulations of the remaining costal cartilages to the sternum are all synovial joints. Cartilaginous joints allow more movement between bones than a fibrous joint but less than the highly mobile synovial joint. The joint between the manubrium and the sternum is an example of a cartilaginous joint.
This type of joint also forms the growth regions of immature long bones and the intervertebral discs of the spinal column. Cartilaginous joints are where the adjacent bones are joined by cartilage. At a synchondrosis the bones are united by hyaline cartilage.
The epiphyseal plate of growing long bones and the first sternocostal joint that unites the first rib to the sternum are examples of synchondroses. What are examples of cartilaginous joints. Cartilaginous joints are one of the three categories of joints in the body the other two being synovial joints and fibrous joints.
These joints allow only a little movement and are called temporary joints because at the age of 18-20 years the epiphyseal cartilage becomes rigid. Examples of primary cartilaginous joints are. The first sternocostal joint.
Neurocentral joints of vertebrae. Joints between the ends and shaft of growing long bones. Primary cartilaginous joint These cartilaginous joints are composed entirely of hyaline cartilage and are known as synchondroses.
Most exist between ossification centers of developing bones and are absent in the mature skeleton but a few persist in adults. Synchondroses related to apophyses. Synchondroses of the pelvis eg.
The middle radioulnar joint and middle tibiofibular joint are examples of a syndesmosis joint. Cartilaginous In a cartilaginous joint the bones are united by fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage. Types of joints with examples.
Types of functional classification join. Synoviol cartilaginous and fibrous. Plane joint hinge joint saddle joint condyloid joint ball.
Cartilaginous synchondroses and symphyses. These joints occur where the connection between the articulating bones is made up of cartilage. For example between vertebrae in the spine.
Synchondroses are temporary joints which are only present in children up until the end of puberty. For example the epiphyseal plates in long bones. Example of synchondrosis joints joint between basilar part of occipital bone with the body of basisphenoid bone.
Symphysis is the fibrocartilaginous joints between symmetric bones in an animals body. These are also known as the secondary cartilaginous joint. Example of symphysis joints pelvic symphysis joints.
Synovial joints in animals. Cartilaginous joints are where the adjacent bones are joined by cartilage. At a synchondrosis the bones are united by hyaline cartilage.
The epiphyseal plate of growing long bones and the first sternocostal joint that unites the first rib to the sternum are examples of synchondroses. Unlike fibrous and cartilaginous joints synovial joints have a joint cavity fluid-filled space between connecting bones. Synovial joints allow for greater mobility but are less stable than fibrous and cartilaginous joints.
Examples of synovial joints include joints in. Some examples of primary cartilaginous joints in humans are the growth plates between ossification centers in long bones. These joints here allow for only a little movement such as in the spine or ribs.
Secondary cartilaginous joints are known as symphysis. These include fibrocartilaginous and hyaline joints which usually occur at the midline. Joints-Know examples of different fibrous and cartilaginous joints Fibrous.
Bones joined by dense fibrous connective tissue no joint cavity most immovable ex. Sutures syndesmoses gomphoses Sutures. Rigid interlocking joints of skull allow for growth during youth contain short connective tissue fibers that allow for expansion in middle age sutures ossify and fuse.
In cartilaginous joints the bones are united with each other by cartilageAgain there is NO JOINT CAVITY. There are two subtypesof cartilaginous joints. Primary cartilaginous joints synchondroses.
A plate of hyaline cartilageconnects the bones at the jointOnly hyaline cartilageis involved and the joints are immoveable. An example is the cartilaginous epiphyseal platewhich separates. An example of a cartilaginous joint is the.
E All of the above. Create an account to start this course today. There are two principal examples.
The atlantoaxial joint between the first two vertebrae and the radioulnar joint at the elbow. At the atlantoaxial joint the dens of the axis projects into the vertebral foramen of the atlas and is held against the anterior arch of the atlas by the transverse ligament. The two types of cartilaginous joints are synchondroses and symphyses.
The epiphyseal plate is an example of a synchondrosis joint while the pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs are examples of symphysis joints.