Homologous structure definition. These structures do not have to look exactly the same or have the same function.
The most important part as hinted by their name is that they are structurally similar.
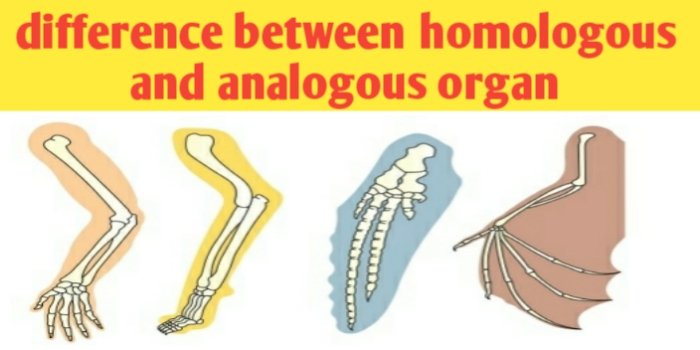
Definition of homologous structure. The definition of a homologous structure is an organ or body part that appears in different animals and is similar in structure and location but doesnt necessarily share the same purpose. An example of a homologous structure is the human arm as compared to the wing on a bird. The definition of a homologous structure is an organ or body part that appears in different animals and is similar in structure and location but doesnt necessarily share the same purpose.
An example of a homologous structure is the human arm as compared to the wing on a bird. A homologous structure is an organ system or body part that shares a common ancestry in multiple organisms. This definition is found in evolutionary biology and uses the meaning of having a.
Homologous structures in organisms are those that have similar structure but different functions. An example of this is the arm of a human and the leg. Homologous structures are organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that by virtue of their similarity suggest their connection to a common ancestorThese structures do not have to look exactly the same or have the same function.
The most important part as hinted by their name is that they are structurally similar. Homologous structures are organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that by virtue of their similarity suggest their connection to a common ancestor. These structures do not have to look exactly the same or have the same function.
What Are Homologous Structures. Homologous structures are similar structures in related organisms. The most important thing to remember about homologous structures is that they share common ancestry.
In other words only organisms that are somehow related to each other can have homologous structures. In science homologous is most often used in the phrase homologous structures which refers to body parts of animals that have a similar structure or origin as in The arms of humans and the limbs of. The word homologous describes any sort of similarity in some ways.
For example if a pair of the chromosome have similar gene sequence and centromere location they are called homologous chromosomes. The homologous structures are exemplified in biology by the same anatomical composition or structural features. Homologous structure definition.
A structure that is present in an organism but no longer serves its original purpose. The most important part as hinted by their name is that they are structurally similar. Homologous structures are part of the body of a species that are anatomically similar to the comparative part of another species.
Having the same relative position value or structure. Having the same or allelic genes with genetic loci usually arranged in the same order homologous chromosomes. A homologous structure in the panda looks like a sixth appendage but it is actually a modified wrist bone that helps the panda pick leaves off the trees more dexterously.
An auditory bone that exists inside the ears of mammals is a homologous structure to a reptiles jawbone including dinosaurs. Definition Of Homologous Organs Homologous Organs can be defined as the organs of different animals that are similar in structure but perform different functions. Homologous organisms share a common ancestry The word Homologous is derived from two Greek words Homo and Logos.
Homo means same and Logos means relations. Therefore the literal meaning of the word Homologous means. A homologous series refers to a series of carbon compounds which have a different number of carbon atoms.
However they contain the same functional group. In this series a group of compounds share similar basic chemical makeup. Also in such a series the compounds show a difference in the number of iterations of a certain aspect of their structure.
What does homologous mean. The definition of homologous is having the same evolutionary origin position or structure. Adjective The wing structu.
In biology homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates where the wings of bats and birds the arms of primates the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Structure of homologous chromosomes.
Homologous chromosomes are chromosomes that contain the same genes in the same order along their chromosomal arms. There are two main properties of homologous chromosomes. The length of the chromosome arms and the location of the centromere.
Homologous - corresponding or similar in position or structure or function or characteristics. Especially derived from an organism of the same species. A homologous tissue graft.
Having a similar position structure value or purpose. Having the same origin although now.