As compact bone grows osteons begin to fuse together. Usually found in long bones of the body it consists of units called osteons each of which is called a haversian system with a series of canals concentric rings and bone cells called osteocytes.
The remainder is cancellous bone which has a spongelike appearance with numerous large spaces and is found in the marrow space.
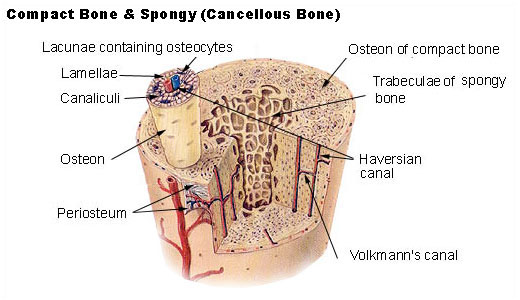
Components of compact bone. Compact bone appears solid and spongy bone consists of a web- or sponge-like arrangement of solidified extracelluar matrix. While compact bone appears at first glance to be solid and uninterrupted closer inspections reveals that the osseous tissue only makes up from 70-95 of the available volume. There are pores and spaces even in compact bone.
In this anatomy course part of the Anatomy Specialization you will learn how the components of the integumentary system help protect our body epidermis dermis hair nails and glands and how the musculoskeletal system bones joints and skeletal muscles protects and allows the body to move. You will engage with fascinating videos. Compact bone as opposed to spongy bone is made of cylindrical units called osteons that are tightly formed together.
As compact bone grows osteons begin to fuse together. The two main structural components typically include spongy bone on the interior with an outer layer of compact bone. Usually found in long bones of the body it consists of units called osteons each of which is called a haversian system with a series of canals concentric rings and bone cells called osteocytes.
Compact bone also called cortical bone dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic ground substance and inorganic salts leaving only tiny spaces lacunae that contain the osteocytes or bone cells. Compact bone makes up 80 percent of the human skeleton. The remainder is cancellous bone which has a spongelike appearance with numerous large spaces and is found in the marrow space.
As seen in the image below compact bone forms the cortex or hard outer shell of most bones in the body. The remainder of the bone is formed by cancellous or spongy bone. Compact bone is formed from a number of osteons which are circular units of bone material and blood vessels.
These units allow compact bone to remain hard and compact while still receiving nutrients from the body and. Terms in this set 4 osteons. Haversian system circular unit which is tightly packed together to form bone tissue.
Circular rings of hardended matrix. Spaces which contain osteocytes. Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces while spongy bone also called cancellous bone has open spaces and is supportive but also lightweight and can be readily remodeled to accommodate changing body needs.
Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of osseous tissue Figure 636. It makes up the outer cortex of all bones and is in immediate. Compact bone also called cortical bone is the hard stiff smooth thin white bone tissue that surrounds all bones in the human body.
It is also called osseous tissue or cortical bone and it provides structure and support for an organism as part of its skeleton in addition to being a location for the storage of minerals like calcium. About 80 of the weight of the human skeleton comes from. Compact bone is made of concentric layers of osteocytes and bony matrix.
Compact bones provide support to mammalian limbs. Moreover it is a storehouse of calcium and hosphorus. Compact bone is laid in such a manner that there are histological units seen in.
What is the difference between compact bone and spongy bone. Compact Bone Osteon Haversion System The basic unit of mature compact bone central canal contains blood vessels lamellae concentric contains bone matrix lacunae each contains an osteocyte canaliculi contain nutrients for osteocytes. A cross section of a compact bone shows concentric circles called lamellae.
When compact bone is studied it is found to be made up of concentric circles called lamellae. Within each lamella collagen is mixed with inorganic minerals like magnesium calcium and phosphorus and layered around a. Compact bone consists of closely packed osteons or haversian systems.
The osteon consists of a central canal called the osteonic haversian canal which is surrounded by concentric rings lamellae of matrix. Between the rings of matrix the bone. Compact bone stands in stark contrast to trabecular bone in several ways.
The functional units of compact bone are osteons. Which contain a centrally located Haversian canal encased in lamellae concentric rings. Osteocytes can be observed in the lacunae between the osteons.
Components of Bone. Bone is a specialised form of connective tissue. Like any connective tissue its components can be divided into cellular components and the extracellular matrix.
There are three types of cells in bone. Osteoblasts Synthesise uncalcifiedunmineralised extracellular matrix called osteoid. This will later become calcifiedmineralised to form bone.
So what are the components of compact bone what is giving the compact bone that tree ring-like appearance. Its these neighboring osteons or these structu. A short lecture by Dr.
Kathleen Alsup introducing students to the components of compact bone within the human bodyCheck out our website LINK BELOW for add. So what are the components of compact bone what is giving the compact bone that tree ring-like appearance. Its these neighboring osteons or these structural units.
Sometimes youll hear osteons referred to as Haversian systems or the eponym in terms of osteons. Thats what is giving this very distinct tree ring-like appearance that you have. Compact bones are also called cortical bones.
Spongy bones are also called cancellous or trabecular bones. Compact bones are made up of osteons. Spongy bones are made up of trabeculae.
Compact bones do not have spaces between lamellae. Components of a Synovial Joint. Structure of Compact Cortical Bone.
Structure of Cancellous Trabecular Bone. Bone Cortical compact bone Periosteum Medullary marrow cavity Capillaries in haversian and Volkmanns canals Capillaries in haversian canals. Compact bone is the denser stronger of the two types of bone tissue Figure.
It can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones where it provides support and protection. Diagram of Compact Bone. A This cross-sectional view of compact.
Compact bone tissue consists of osteons that are aligned parallel to the long axis of the bone and the Haversian canal that contains the bones blood vessels and nerve fibers. The inner layer of bones consists of spongy bone tissue. The small dark ovals in the osteon represent the living osteocytes.
Modification of work by NCI NIH. Select all components of the appendicular skeleton. Bones of the arms and legs pelvic girdle pectoral girdle skull vertebral column rib cage.